What is stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy can be defined as the medical use of stem cells to cure or prevent any ailment or any other morbid medical condition.
Stem cells which are the pillars of stem cell therapy are undifferentiated biological cells that can differentiate into distinct specialized cells. These specialized cells can even differentiate further to produce more stem cells.
Stem cell treatment came to be, through years of research put in by many scientists and other medical professionals. Some of the notable ones include the duo Ernest McCulloch and James Till, Andy Becker, Lou Siminovitch, Georges Mathé, Martin Evans, Matthew Kaufman, and James Thompson. There are others whose groundbreaking work helped expand further on our knowledge of stem cells and it's used, but they are too many to mention.
Stem cell therapy though formerly an alien concept, is now prevalent in many developed countries. It is known to treat a host of diseases like cancers, sickle cell anemia, osteoarthritis, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, and many more.
A lot of medical institutions provide stem cell treatment services, an example of which is Swiss Medica clinic.
How stem cell therapy works
Stem cell therapy is a procedure that involves the harvesting of stem cells from:
- Human bone marrow- Usually harvested from the femur or iliac crest.
- Adipose tissue- Gotten from the abdomen through liposuction.
- Blood- Extracted through apheresis.
- Umbilical cord blood- Just after the birth of a child.
- Embryonic stem cells- Isolated from the inner cell mass of blastocysts. Embryonic stem cells are not being widely applied in medical practices because most laws prohibit their use.
The stem cells gotten from the above sources are then cultivated in the laboratories of medical institutions that offer stem cell therapy for patients.
After cultivation, the stem cells are injected into the patient's body through various routes, for example, intravenous, local or intracerebral routes.
After the treatment, the patient would be left to recover whilst being monitored by the doctors to detect any possible complications that may arise from the operation.
The stem cell treatments are usually successful and patients are offered a better life quality after the procedure.
Stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes
Brief description of type 2 diabetes
Diabetes type 2, also known as diabetes mellitus type 2, is the most common long-term metabolic disorder.
This happens when the body becomes unable to utilize glucose to produce energy, leading to its accumulation in the blood. This can only lead to negative outcomes. Type 2 diabetes is characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels, the anomaly of insulin-producing organ – the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency, and the body's resistance to the insulin produced.
Some symptoms of type 2 diabetes include inexplicable weight loss, uncontrolled thirst and frequent urination, increased hunger, fatigue, and the inability of sores and wounds to heal. The manifestation and progression of these symptoms often occur slowly.
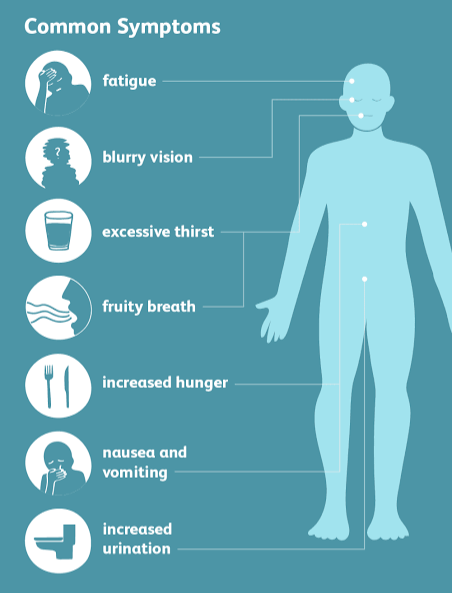
Image 1. Symptoms of diabetes.
Causes of type 2 diabetes include genetic predisposition, obesity, lack of exercise, and advancement in age. Previous cases of other types of diabetes like gestational diabetes is also a risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes has some long term complications and these include: cardiovascular diseases, diabetic retinopathy which can result in blindness, kidney failure, strokes, decreased blood flow to body extremities which could lead to amputation, decreased life expectancy, and many others.
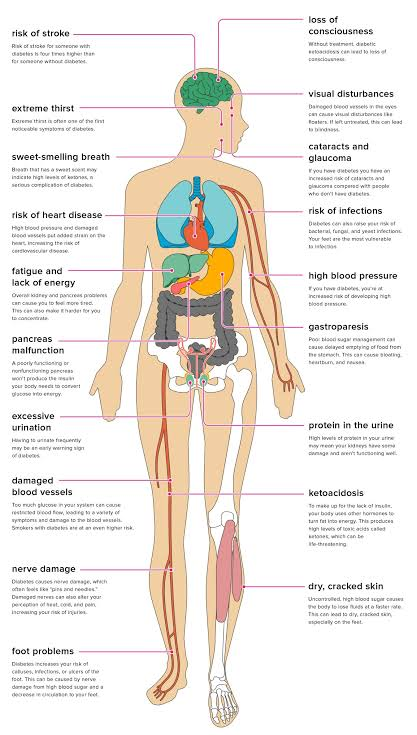
Image 2. Complications of diabetes.
Diabetes type 2 can be diagnosed with the use of blood tests like oral glucose tolerance test and fasting plasma glucose.
Ways of preventing type 2 diabetes include: maintaining healthy body weight, maintaining a healthy diet, and proper regular exercise.
Treatment of diabetes type 2 involves implementing dietary changes to lower blood sugar levels, exercising more frequently, and prescribing medication like Metformin. Some people also require routine insulin injections and other obese patients might require bariatric surgery.
Stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes
Stem cell therapy for type two diabetes involves the use of bone marrow stem cells that have been isolated from the bone marrow or another tissue of a patient or that of a donor, to treat the patient.
Bone marrow or adipose tissue stem cells are used mainly because they are present in high quantities, and because they possess special immune-regulating characteristics. They are also much safer to use as they present no danger to a patient's health.
Steps involved in receiving stem cell treatment
- 1. Harvest- This process involves the harvesting of bone marrow cells from the iliac crest of either the patient or a donor through a minimally invasive bone marrow aspiration operation. This takes about thirty minutes to an hour.
- 2. Cultivation- After the harvest, the bone marrow is then taken to the lab for isolation, cultivation, and activation.
- Administration- The cultivated bone marrow stem cells are then administered to the patient to begin the healing process. The stem cells can be administered either intravenously or via direct site injections.
Stem cell therapy offers periods of relief from the symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
Even though there is no strong evidence of stem cell therapy being able to completely cure the disease, receiving stem cell treatment can however significantly improve a patient's life quality by alleviating the symptoms, moderating the effects of its progression, and decreasing the complications related to type 2 diabetes.
In patients receiving stem cell diabetes treatment, high levels of improvement have been noticed in several areas such as lowering of blood sugar levels leading to stable blood sugar levels, a decrease in the level of severity of other related diseases, and an overall increase in normal body functions.
Expected outcomes of the use of stem cell therapy in treating type 2 diabetes
- Reduced severity of clinical symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
- The decrease in serum C-peptide.
- The decrease in the concentration of glycated hemoglobin.
- Postponing the development of complications.
- General overall life improvement.
How stem cell therapy is used to treat type 2 diabetes
The stem cell treatment for type 2 diabetes involves the use of stem cells to primarily reduce blood sugar levels by stimulation of pancreas to produce more insulin and prompting the body to make use of the insulin produced.
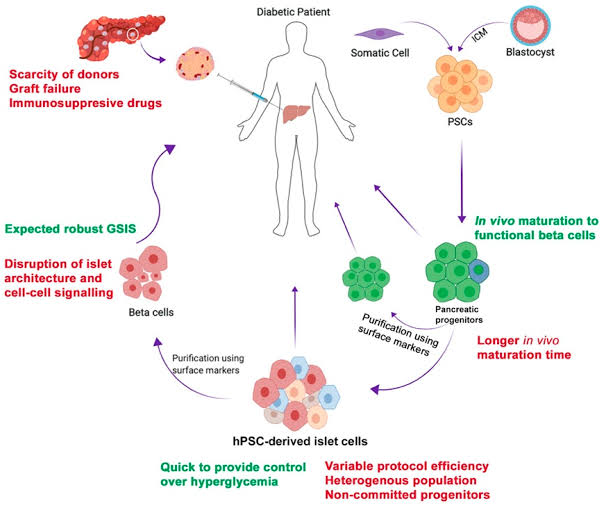
Image 3. Stem cell therapy for diabetes.
How stem cell therapy works for type 2 diabetes:
- Activating progenitor cells of the pancreas and causing them to differentiate, thereby increasing the number of beta-cell precursors.
- Increasing vascularisation in the islets of the pancreas, leading to the improvement of pancreatic function and enhancement of its endocrine function.
- The development of an autoimmune component which has an immunomodulatory effect.
How safe are stem cells treatment for diabetes type 2?
Stem cell treatments are generally considered safe, but like every other medical procedure, there are risk factors. However, more research is being done to further expand on its benefits and eliminate all possible risks.
Stem cell therapy for diabetes type 2: cost
One of the limitations of the use of stem cell therapy is its cost.
Given that it is still being developed and research materials aren't readily available, the cost of stem cell therapy is very high. It has a range of $5,000 to $50,000 depending on factors such as a source of stem cells, type of stem cells, patient's medical history, and a number of procedures required.
On average, the cost of stem cell treatment for diabetes type 2 is about $12,000 to $35,000.
Fetal stem cell therapy for diabetes type 2
Fetal or embryonic stem cells are believed to be the best stem cells for medical purposes because they have a high level of division and are multipotent. These stem cells are harvested directly from the human blastocyst and this could lead to the destruction of the blastocysts and abortion. Because of this reason, there are many moral, philosophical, ethical, and religious barriers preventing the use of embryonic stem cells. So that area of stem cell research is relatively unexplored.
Advantages of stem cell therapy in treating type 2 diabetes
- Increases life expectancy.
- Alleviates symptoms.
- Improves patient life quality.
- Has minimal side effects.
- Well tolerated at any age.
Type 2 diabetes and stem cell therapy: Its relevance in the medical field
Does stem cell therapy work for type 2 diabetes?
Yes, it does.
It helps mitigate the symptoms of type 2 diabetes and it could give an individual the chance to live a relatively normal and healthy life. It also leads to an increase in the life expectancy of an average diabetic patient.
Stem cell therapy for diabetes is already happening and more research is being done to explore all the ways to make it better.
Since the increase in age predisposes one to the likelihood of having diabetes type two, it could be said that people that are up to 40 and above have a higher chance of having type two diabetes. Stem cell therapy for diabetes is also an option for patients aged 40 and above.
Even though stem cell therapy doesn’t completely cure type 2 diabetes, it generally improves a patient's life quality, reduces symptoms, moderates the effects of complications arising from other diseases, and increases life expectancy.
I am an author and Publisher on self-growth.
Post new comment
Please Register or Login to post new comment.